Homework Assignment for 3.9 and 3.11
Completing the Hacks given to us for Unit 3, Sections 9 and 11
- This Group: Eli, Trent, Khalid, and Samarth
- 3.9 Video 1
- Lesson Practice
This Group: Eli, Trent, Khalid, and Samarth
3.9 Video 1
Notes
- Algorithms can be written in different ways and still accomplish the same tasks and this also means that the algorithms can appear similar yet yield different side effects or results
- Some conditional statements can be written as equivalent Boolean expressions
- Some Boolean expressions can be written as equivalent conditional statements
- Different algorithms can be developed or used to solve the same problem
- Algorithms can be created from an idea, either by combining existing algorithms, or by modifying existing algorithms
- Knowledge of existing algorithms can help in constructing new ones. Some existing algorithms include
- Determining the maximum or minimum value of two or more numbers
- Computing the sum or average of two or more numbers
- Identifying if an integer is or is not evenly divisible by another integer
- Determining a robot’s path through a maze
- Using existing correct algorithms as building blocks for constructing another algorithm has benefits such as reducing development time, reduce testing, and simplifying the identification of errors
- For binary search algorithms
- Determine the number of iterations required to find a value in a data set.
- Explain the requirements necessary to complete a binary search.
- The binary search algorithm starts at the middle of a sorted data set of numbers and eliminates half of the data; this process repeats until the desired value is found or all elements have been eliminated.
- Data must be in sorted order to use the binary search algorithm
- A binary search is often more efficient than sequential/linear search when applied to sorted data
- There are two important ways to search a list
-
Sequential Search
- It doesn’t have to be in order
- For a Sequential Search you compare each number to the number you are searching for
- You can also use this method for strings as well
-
Binary Search
- While using Binary Search you have to put the group of numbers from ascending or descending order
- What the computer does it takes the lowest index and the highest index, adds them and then divides that value by 2
- This gets the middle value and starts the search at the middle of the group
- Go to the respective index and pull the element, if this is not the desired number then go to the left and the right to and repeat the same process for the left and the right without including the index of the middle number
- To put the efficiency of the binary search method into context if you have a list of 600 numbers the maximum amount of attempts it will take to get the number is 10. (1 level of tree is one search, the algorithm goes to the side of which the number is on the tree)
- This method also applies to strings as well because only the indexes are getting compared
- As long as the user can put it in an order (preferably alphabetical order) to tell the algorithm which side of the middle index to go to next then it is possible to use
Vocab
- Iteration: Repeating steps, or instructions over and over again (this could be also often called a loop)
- Selection: is a decision or question. At some point in an algorithm there may need to be a question because the algorithm has reached a step where one or more options are available
- Algorithm: A process or set of rules to be followed in calculations or other problem solving operations, especially by a computer.
Lesson Practice
Here are some notes that I took during the lesson as well as the practice problems
Dice Problem
Do these two algorithms give the same results?
My Answer: No
Explanation: The code is different and it will result in different outputs for specific answers, this is because the the indents are not correct and will run multiple for specific values. Take the number 5 for example, the first algorithm will give you an output of “Nice Roll!” while the second algorithm will actually output two lines, “Nice Roll!” and “Meh… You can do better”. This is because there is nothing telling the code not to run the second line of code, because it is just if statements.
print("What did you roll on the dice?")
diceRoll = int(input())
if diceRoll >= 4:
print("Nice roll!")
else:
if diceRoll >= 2:
print("Meh... You can do better")
else:
print("That was not a great roll!")
print("What did you roll on the dice?")
diceRoll = int(input())
if diceRoll >= 4:
print("Nice roll!")
if diceRoll >= 2:
print("Meh... You can do better")
if diceRoll < 2:
print("That was not a great roll!")
- In what instances do the algorithms yield different results for the same input?
My Answer: When the input is 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, or greater if the dice has more than 6 sides
Explanation: When you plug these values the code is just doing what it is told, any number that is greater or equal to 2, will have a different output than the first algorithm. We need to find out a way in order for the algorithm to realize what we want it to do.
- Why does this happen?
Explanation: As I have mentioned earlier, this happens because the code is just doing what it is told and nothing is there that is telling the code that it can not work. In order to fix this problem, we can just add like a different domain sort of in the code, so that way if the value is greater than or equal to 2 and less than 4, it will output that line. We need to tell the code to specifically only run certain lines of codes, even if the statement is true. You can look at the code after this section to help you really understand what you really need to do.
Can we adjust the second algorithm to yield the same results?
print("What did you roll on the dice?")
diceRoll = int(input())
if diceRoll >= 4:
print("Nice roll!")
if diceRoll >= 2 and diceRoll < 4:
print("Meh... You can do better")
if diceRoll < 2:
print("That was not a great roll!")
Important Takeaways
- Small changes/mistakes can have a big impact on the result
- You need to make sure the code will work how you want it to
- There is often more than one way to achieve the same result
- You can add multiple if and else statements in order to make sure you get the result you want
- It is very useful to put multiple if statements inside of one another
Conditional vs Boolean
-
How could this conditional scenario be replaced with a boolean scenario?
- IF (isHoliday)
- {
- school⟵false
- }
- ELSE
- {
- IF(isWeekday)
- {
- school⟵true
- }
- ELSE
- {
- school⟵false
- }
- }
What needs to be true and what needs to be false in order for you to go to school?
In order for school to be true, the day can not be a holiday nor can it be a weekend. If the day is a holiday, then the code will stop there and you do not need to go to school, but if it is not a holiday, then it will check and see if it is a weekday, and if it is a weekend, then there is no school, but if there it is a weekday and it is not a holiday, then there is school.
- First conditional: If isHoliday is true, you do not need to go to school
- Second conditional: If isWeekday is true, you do need to go to school. However, if it is false, school also becomes false
Therefore, in pseudo code, this statement could be written as:
- school⟵((NOT (isHoliday)) AND (isWeekday))
- Keep in mind that both of these statements yield the same results, and neither of them are incorrect
More Comparing Algorithms
The algorithms below are to sum the odd numbers from 1 to 9 (1+3+5+7+9). Do they each work as intended? Yes they both do work as intended because 1+3+5+7+9 is 25, and each code segment will output 25
-
- sum⟵3
- counter⟵1
- REPEAT 4 TIMES
- sum⟵sum + counter
- counter⟵counter + 2 - DISPLAY sum Sum: 25
-
- sum⟵0
- counter⟵9
- REPEAT UNTIL counter < 1
- sum⟵sum + counter
- counter⟵counter - 2 - DISPLAY sum Sum: 25
Why is it important to understand that algorithms can be written in different ways and still accomplish the same tasks?
It is important to understand that algorithms can be written in different ways and still accomplish the same tasks because you can use them in different ways and when coding, it is important to know that your algorithm is not necessarily the correct one, but it could be the most efficient or easy to understand one.
Create an Algorithm
Code for This Problem
- REPEAT UNTIL (goalReached)
- {
- MOVE_FORWARD ()
- ROTATE_RIGHT ()
- MOVE_FORWARD ()
- ROTATE_LEFT ()
- }
Practice Question
Choose which algorithm that uses selection and/or iteration to determine the cost of one item in the store is correct
The display at the store says the following:
All Green Tag Items - 25% off All Red Tag Items - 60% off
Suppose that the tax on all items is 10%
Algorithm A:
- DISPLAY (“What is the cost of the item?”)
- cost←INPUT ()
- IF (greenTag)
- {
- cost ← 0.75 * Cost
- }
- IF (redTag)
- {
- cost ← 0.40 * Cost
- }
- cost ← 1.10 * cost
Algorithm B:
- DISPLAY (What is the cost of the item)
- cost←INPUT ()
- IF (greenTag)
- {
- cost ← 0.75 * Cost
- }
- IF (redTag)
- {
- cost ← 1.10 * cost
- }
- cost ← 0.40 * Cost
Another Robot Example
How can we make this work?
- Create a algorithm to move the robot to the grey square for the grid above
- The robot is represented by a triangle
-
The robot can move into white and grey squares but cannot move into a black square


- What is wrong with the algorithm above?
- How do we fix this?
- By allowing it to move left
Practice Problems
-
Which is a plausable way to pattern your numbers for binary search.
a. [1,4,5,2,3] b. [24,22,23,28,30] c. [5,6,7,8,2] d. [1,2,3,4,5] My Answer: d
Explanation: When using Binary search, you want to make sure that the numbers in the list is actually in order from least to greatest, and option d is the only list that does this
-
How many checks would it take to print out 20 using sequential search
- [1, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 10, 20] 7 Checks
Explanation: This is because 30 is at the end of the list, and you are using sequential, so you have to inspect each item in the list, and since 20 is the 8th term, it would take 7 checks
-
How many checks would it take to print out 30 using binary search
- [1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9, 11, 30] 5 Checks
Explanation: Binary Search starts in the middle of the list and then checks both sides, it will take 5 checks until it finds 30 since it is at the end of the list
-
Using Binary Search how many checks would it take to find the word kiwi.
- [Apple, Banana, Kiwi, Mango, Strawberry] 1 Check
Explanation: If using Binary Search, Kiwi is in the middle of the list so it makes it easy to find because it will find Kiwi with one check
Rap
- Each group has 2 minutes to write a 3 line rap about what they learned. One volunteer will rap their group’s lines and will receive a reward
Our Group Rap:
Binary Search has a lot of potential, It is just essential, Way better than sequential,
Hacks
- Write this Boolean statement in the form of a conditional (if/else) statement: stayInside⟵((isCold) OR (isRaining))
print("Let's Check to see if we can go outside today")
isCold = True
isRaining = True
stayInside = []
if (isCold or isRaining) {
stayInside = True
print("You Should Stay Inside!")
}
else {
stayInside = False
print("You Can Go Outside!")
}
-
Create an algorithm that uses selection and/or iteration that will represent one player’s complete turn.
-
During a turn, each player gets 4 attempts/chances to get the greatest number possible.
-
During each attempt, the player will use a random number generator to select a random number from 1 to 10.
-
After they have had 4 chances, their score is the greatest number they received from the random number generator, and their turn is over.
-
import random
attempts = []
i = 1
while i <= 4"
attempts.append(random.randint(1,10))
i = i + 1
print("These Are Your Numbers" + attempts)
print("Highest Roll:" + max(attempts))
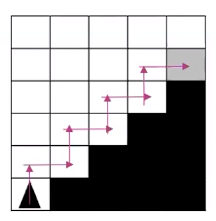
- Create an algorithm that will allow the arrow to reach the gray square: finish = false
while finish = false: if canMoveForward = true: moveForward() else: if canMoveRight = true: turnRight() moveForward() if touchingFinish = true: finish = true break()
I used a while loop so that it will keep running until it finishes and then if the robot is touching the finish line then the code will stop. It will move forward until it hits the black block and then it will turn right and move forward, until it hits the edge so it will run through the if statement again and turn right.
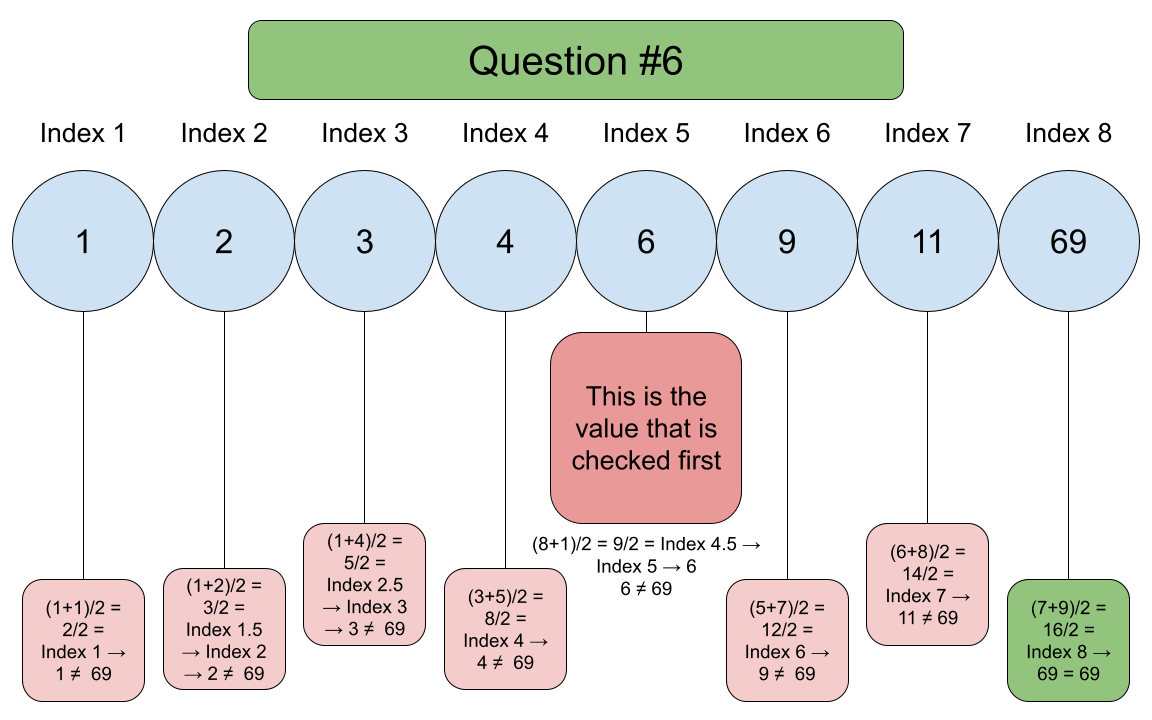
- Make a binary search tree of different the list [1,2,3,4,6,9,11,69]
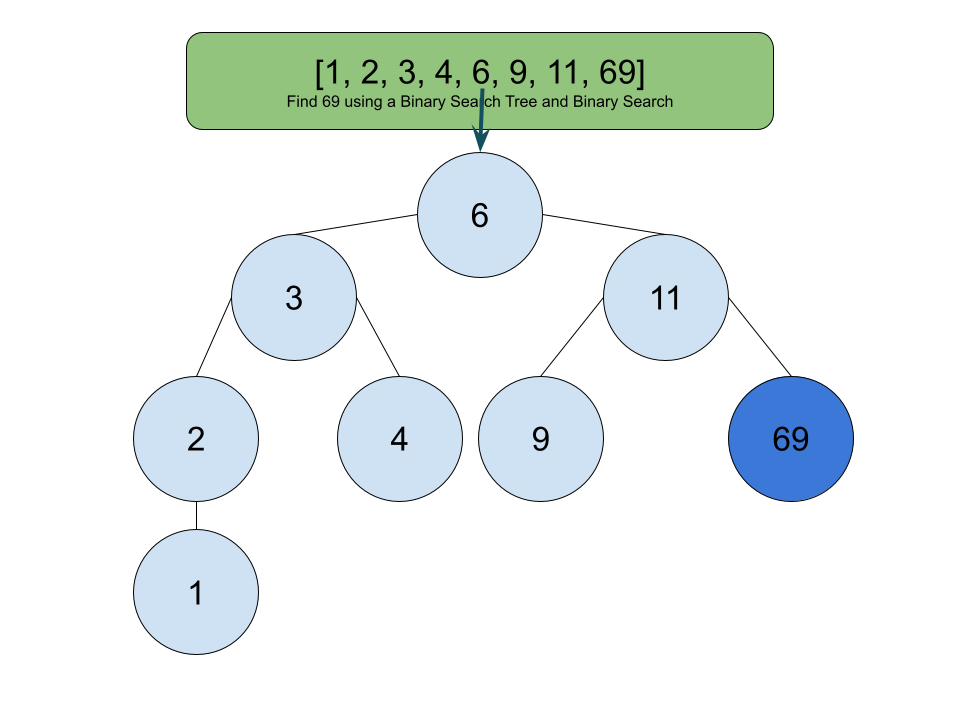
- Explain thoroughly how to find the number 69 in the list above (use key words)
We can check the number and search for 69 in the array by splitting it. You need to index the list and find the middle value of it, since the number of items in the list is even, so the middle number would be 6 which would still be less than 69. This means that we have to keep looking at the right and left side of the list. After 3 more searches, you can finally find the value 69. Otherwise you can use sequential search which would take longer because you are looking all the way at the beginning at the list and 69 is at the end.
-
Make a diagram explaining how you found the list (not tree, include equation)
-
Put this list of strings in a order that can be used for binary search [“store”,”Market”,”Walmart”,Target”,”Ralphs”]
search [“Market”, “Ralphs”, “store”, “Walmart”, “Target”]
You can use Binary Search for this list and then use it, I am not really sure if I did it right, but this seemed to make the most logical sense. I chose this because they are all markets, but market and ralphs are really for produce, but at target and walmart, they are more like retail stores.
- Explain why Binary Search is more efficient than Sequential Search
Binary Search is more efficient than Sequential Search because it allows us to index through lists much more efficiently and it allows us to be able to find out and search for items much more quicker. Binary Search helps us to search exponentially while sequential search moves through a list one by one. Binary Search actually is able to index through half the list every single iteration, so it is much more quicker. Binary Search can save a lot of time compared to Sequential Search.
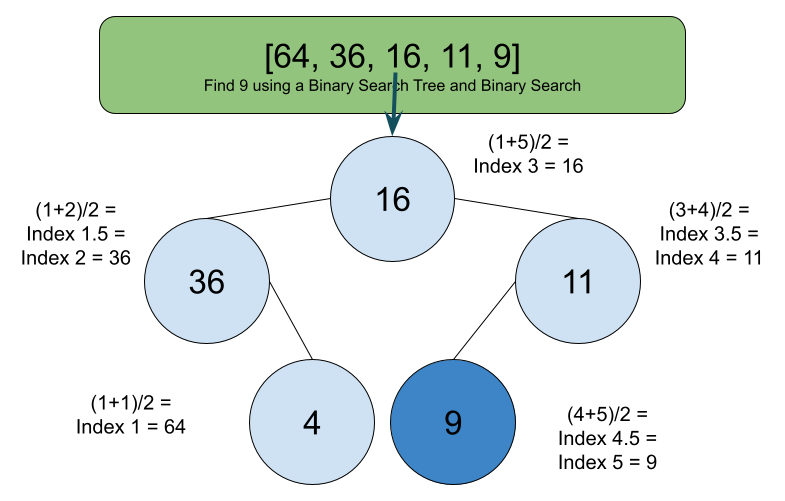
- [64,36,16,11,9] Explain which number you are finding, how many check it would take, and make a binary search tree
I am going to choose to find the number 9 which is at the end of the list, but if using binary search, it should only take us two checks. I think this list should work without any reordering because it is from highest to lowest, and usually I do lowest to highest, but if doing code we should switch the > to a < so the code knows where to search.